What is Magnesium Glycinate? Benefits, Uses, and Molecular Structure Explained
Magnesium glycinate is a popular dietary supplement lauded for its high bioavailability and gentle impact on the digestive system. It provides the essential mineral magnesium, crucial for hundreds of bodily functions, bound to glycine, an amino acid known for its calming properties. Let's explore the science behind this compound.
Understanding Magnesium Glycinate: The Basics
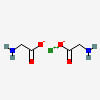
Magnesium glycinate, also known as magnesium bisglycinate, features the molecular formula C4H8MgN2O4 and the PubChem CID 84645. It's formed when magnesium binds with two glycine molecules.
This chelation (binding) process enhances magnesium's absorption in the small intestine, reducing the likelihood of digestive side effects often associated with other forms of magnesium.
Why Choose Magnesium Glycinate Over Other Forms?
Bioavailability is key! Magnesium oxide, for instance, has poor absorption rates compared to magnesium glycinate. This means your body can utilize a higher percentage of magnesium from the glycinate form, leading to more effective results.
Consider this simple comparison:
- Magnesium Oxide: Lower bioavailability, may cause digestive upset.
- Magnesium Citrate: Better bioavailability than oxide, but can still have a laxative effect.
- Magnesium Glycinate: High bioavailability, gentle on the stomach.
Key Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate: What Can It Do For You?
Magnesium is vital for numerous physiological processes. Magnesium glycinate is often used to address deficiencies and support overall health. Here are some potential benefits:
- Improved Sleep Quality: Glycine promotes relaxation and may improve sleep patterns. Magnesium also is essential for nerve cell communication, which can calm your nervous system for more restful sleep.
- Reduced Anxiety: Both magnesium and glycine can have calming effects on the nervous system, potentially reducing anxiety symptoms.
- Muscle Relaxation: Magnesium helps regulate muscle contractions and may alleviate muscle cramps and spasms.
- Bone Health: Magnesium is a crucial component of bone tissue and contributes to bone density.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Magnesium plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Delving into the Molecular Details
Let's examine key molecular properties of magnesium glycinate:
- Molecular Weight: 172.42 g/mol
- IUPAC Name: magnesium;2-aminoacetate
- Molecular Formula: C4H8MgN2O4
The presence of glycine enhances the solubility and absorption of magnesium within the body.
Common Uses and Applications of Magnesium Glycinate Supplements
Magnesium glycinate is widely available as a dietary supplement. Here's how it's commonly used:
- To combat magnesium deficiency: Many people don't get enough magnesium through diet alone.
- To support sleep: Taken before bed, it can promote relaxation.
- To manage anxiety: Helps regulate the nervous system.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the appropriate dosage for your needs.
Safety Considerations and Potential Side Effects
Magnesium glycinate is generally considered safe for most people when taken as directed. However, high doses may cause diarrhea, nausea, or abdominal cramping.
Important note: Individuals with kidney problems should consult their doctor before taking magnesium supplements.
Magnesium Glycinate: A Closer Look at the Components
Magnesium glycinate is made up of two essential components:
- Magnesium (Mg): An essential mineral involved in over 600 enzymatic reactions.
- Glycine (C2H5NO2): An amino acid with calming and neuroprotective properties.
Decoding the Chemical Identifiers
Here's a quick reference to identify magnesium glycinate:
- CAS Registry Number: 14783-68-7
- UNII: IFN18A4Y6B
- DrugBank ID: DB11189
Concluding Thoughts: Is Magnesium Glycinate Right For You?
Magnesium glycinate offers a highly absorbable form of magnesium with a lower risk of digestive side effects. If you're looking to boost your magnesium intake to potentially improve sleep, reduce anxiety, or support overall health, magnesium glycinate might be a suitable option. But remember to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if it's beneficial for your specific needs.




%3Amax_bytes(150000)%3Astrip_icc()%2FGettyImages-1500286867-b1bd2c13d9f64f4faf4741ac385b03e0.jpg&w=3840&q=75)



